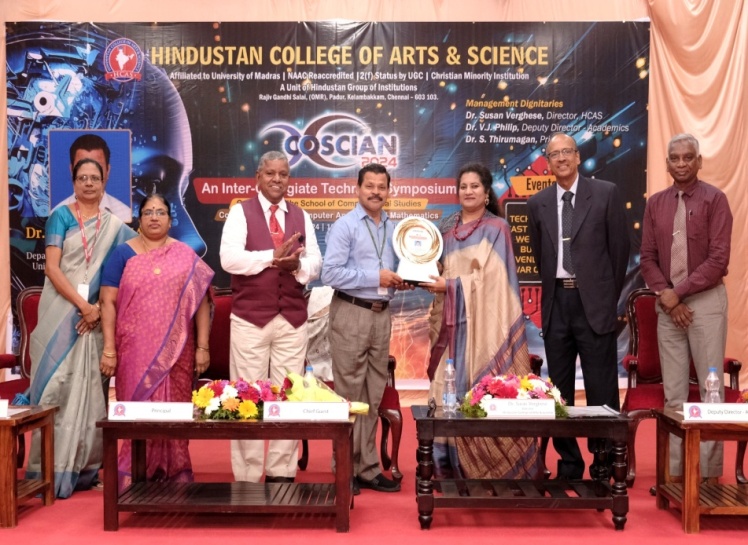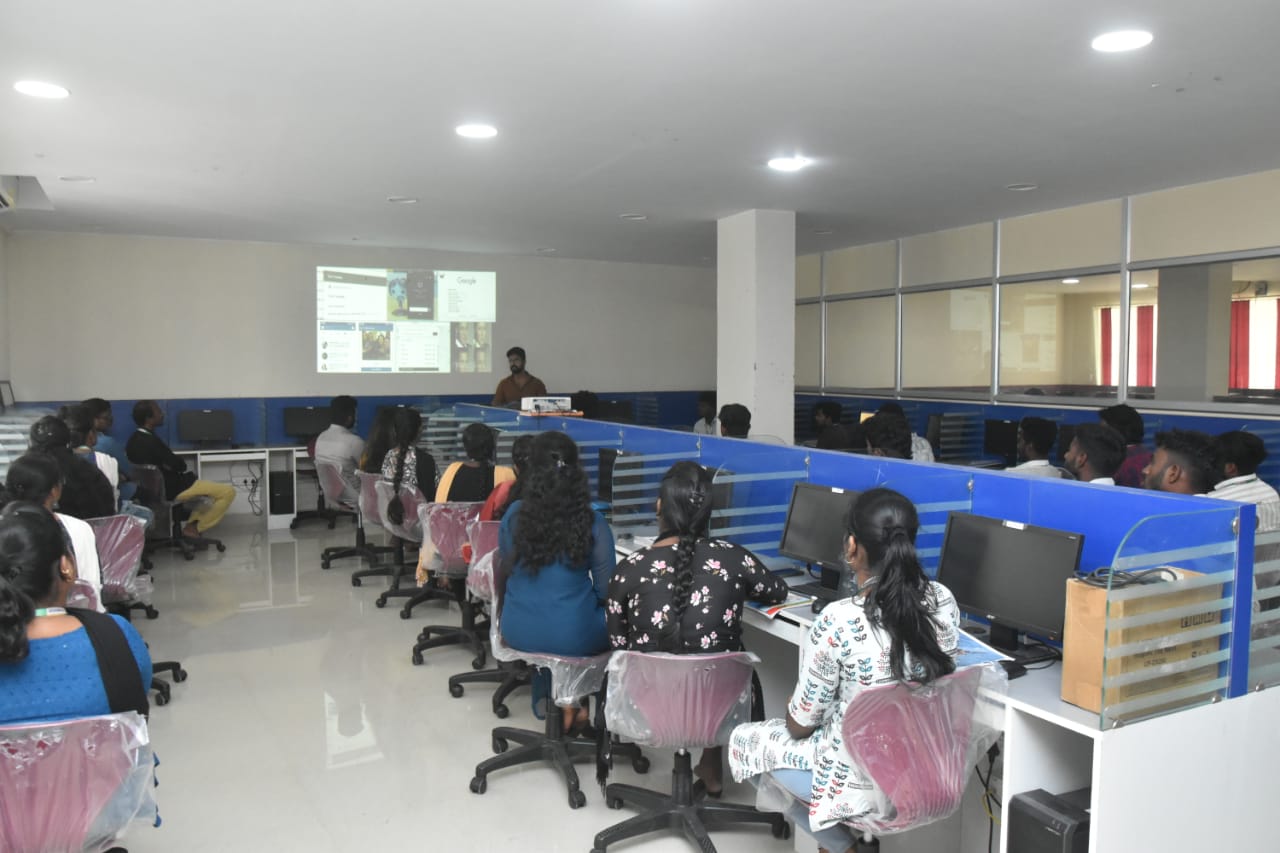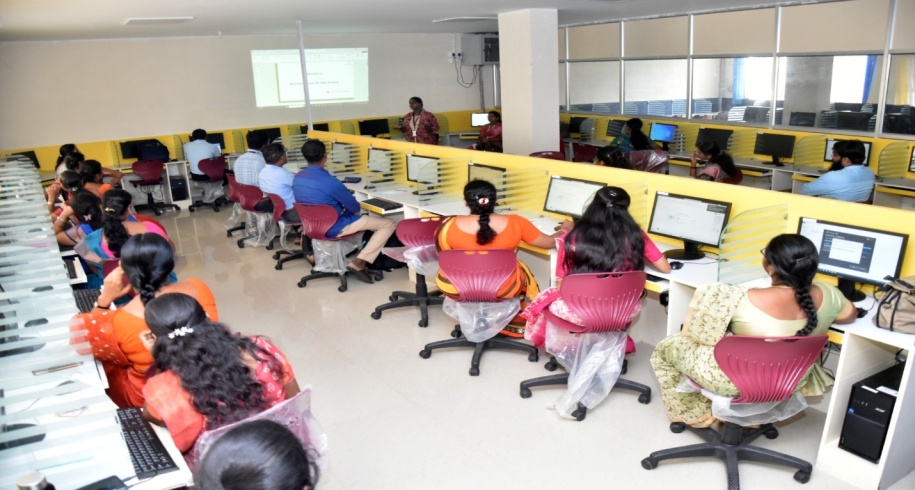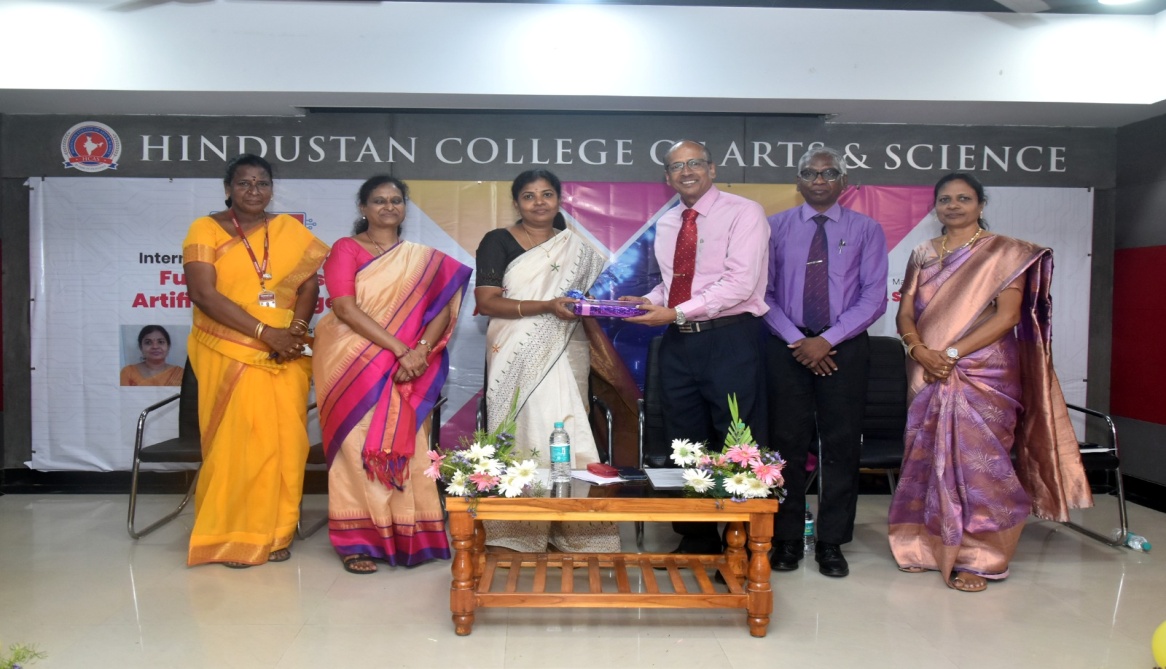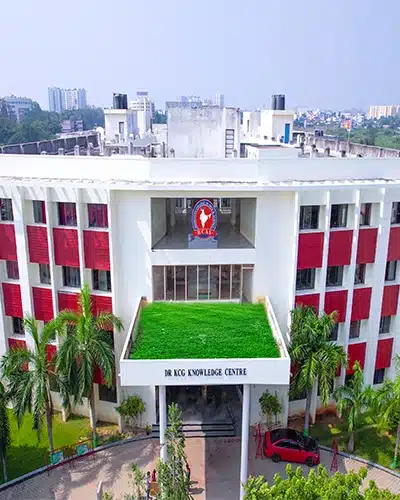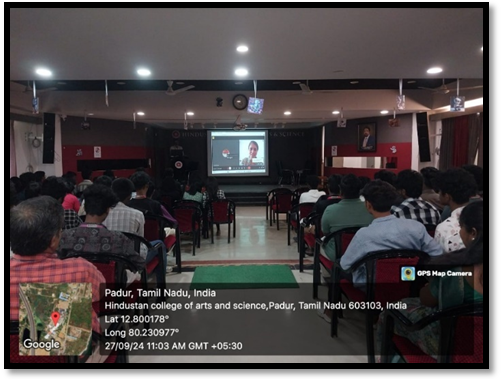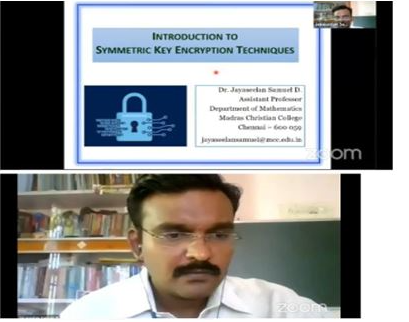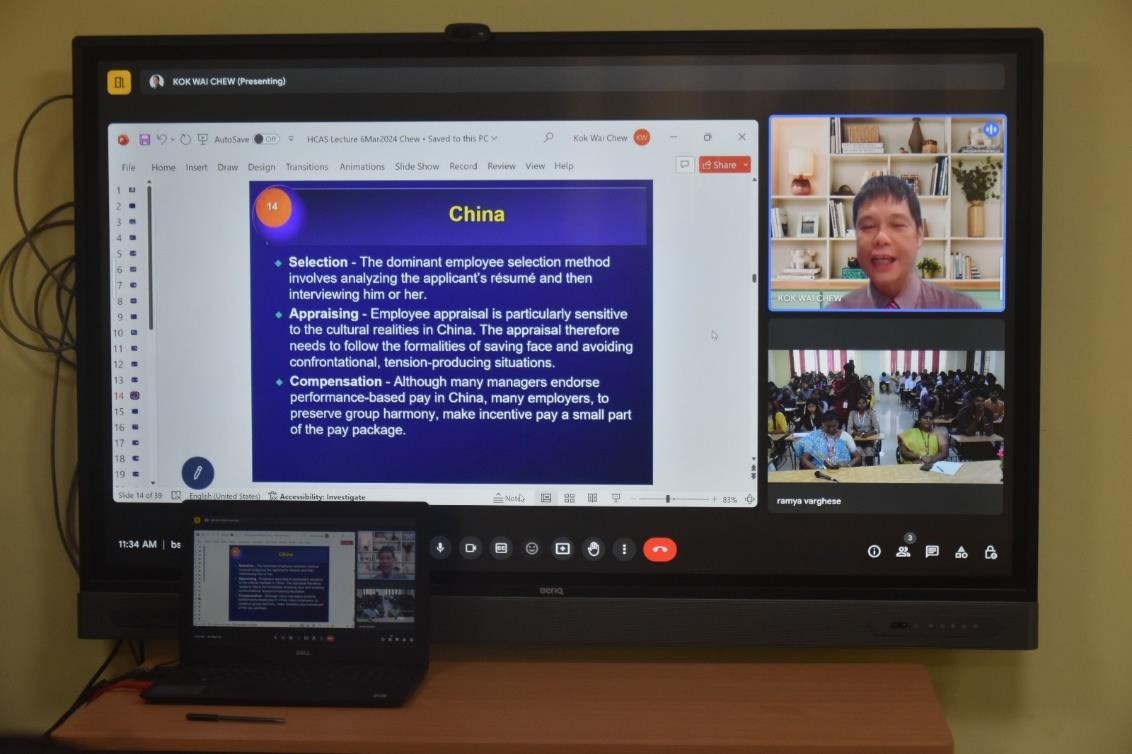

 about our Department
about our Department
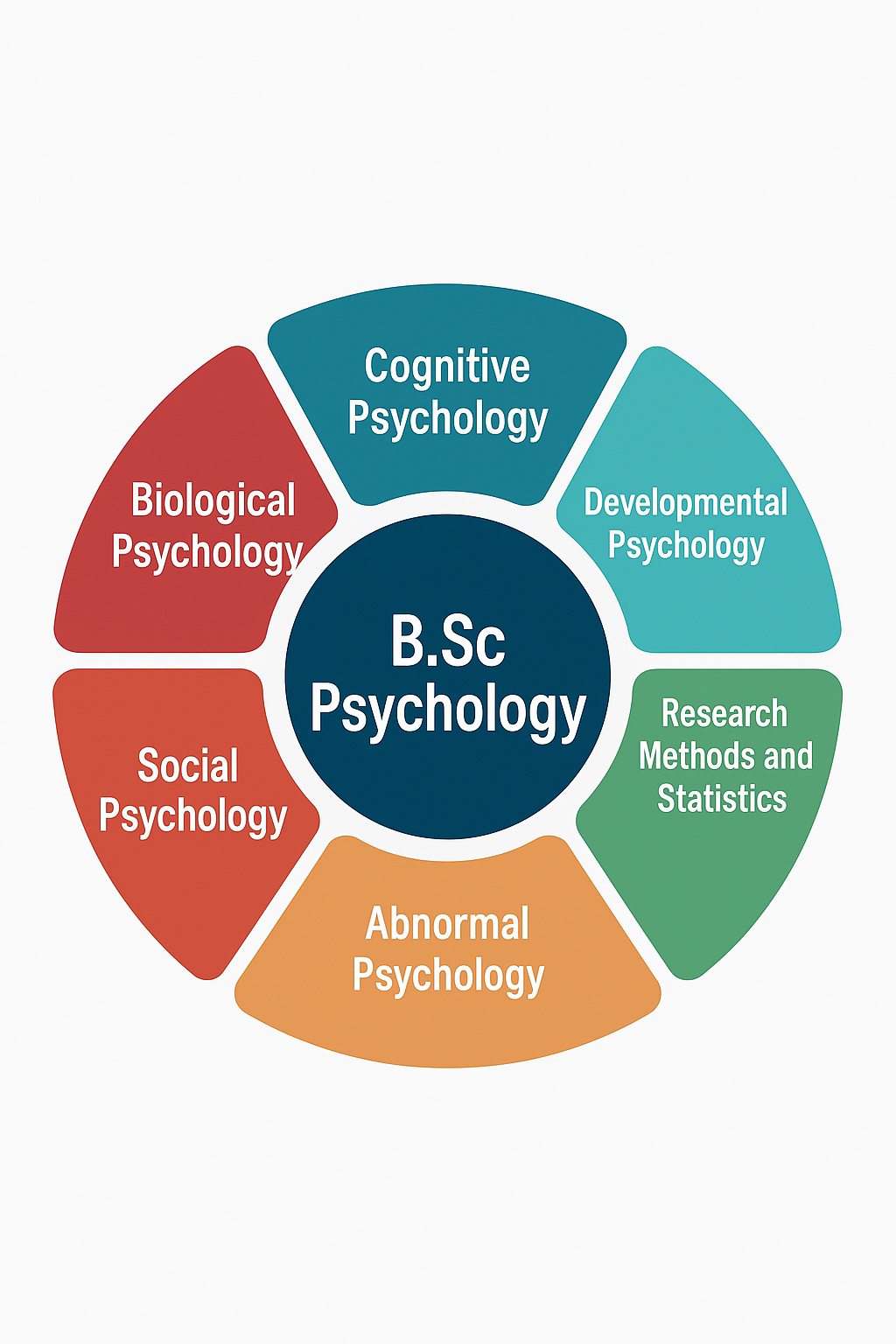
A Bachelor of Science (B.Sc) in Psychology is an undergraduate program that combines scientific principles with the study of human behavior and mental processes. This degree focuses on understanding cognitive, emotional, and social behaviors through research, analysis, and practical applications.
- Library
- Best Laboratories
- Add-on Courses
- Scholarships









 Choose the right course today
Choose the right course today










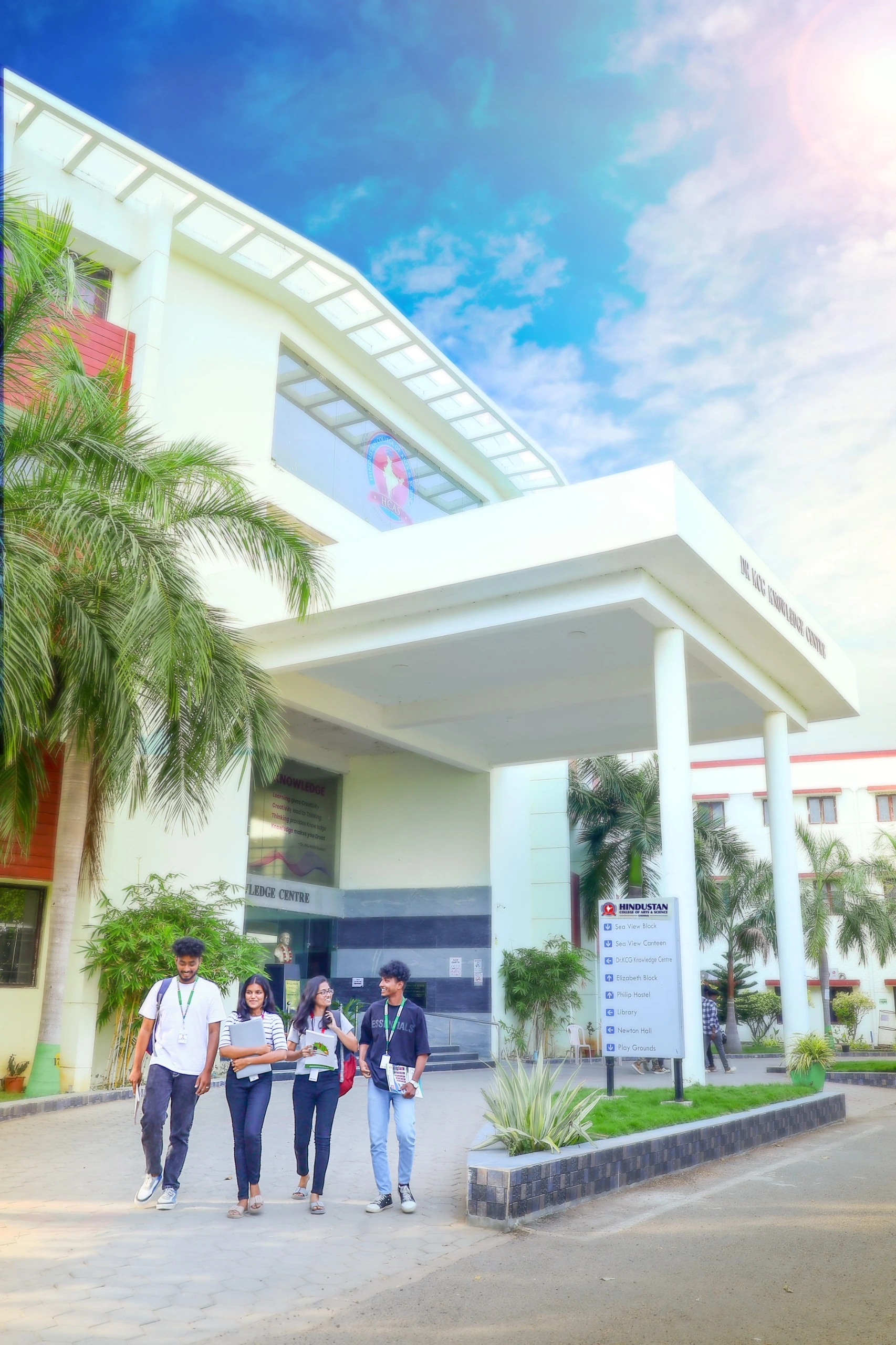
 Shaping Futures
Shaping Futures